Working Time
| Monday - Saturday | 06:00 pm to 09:00 pm |
| Sunday | 08:00 am to 10:00 am |
| Monday - Saturday | 06:00 pm to 09:00 pm |
| Sunday | 08:00 am to 10:00 am |
Introduction:
Hernias are a common medical condition that can affect people of all ages, genders, and backgrounds. Despite their prevalence, there's often confusion and misconceptions surrounding hernias. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore everything you need to know about hernias, including their causes, symptoms, types, diagnosis, and available treatment options.
What is a Hernia?
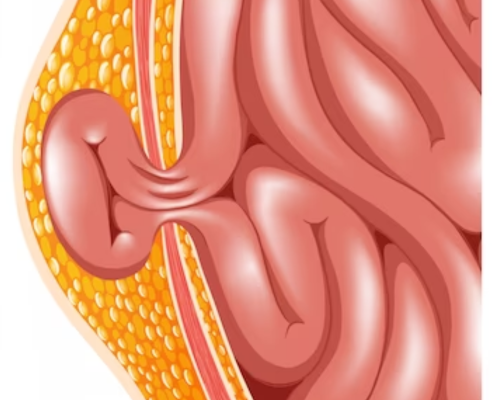
A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. This can result in a visible bulge or lump, often accompanied by discomfort or pain. While hernias can develop in various areas of the body, they most commonly occur in the abdomen.
Causes of Hernias:
Muscle Weakness:
Hernias often develop in areas where the muscles are naturally weaker. Factors such as age, genetics, and certain medical conditions can contribute to muscle weakness, increasing the risk of hernia formation.
Strain and Pressure:
Heavy lifting, persistent coughing, straining during bowel movements, and pregnancy can exert increased pressure on the abdominal muscles, potentially leading to the development of a hernia.
Congenital Factors:
Some individuals may be born with a predisposition to hernias due to congenital factors. Weaknesses in the abdominal wall present from birth can become more pronounced over time, leading to herniation.
Obesity:
Excess body weight and obesity can contribute to the development of hernias. The added pressure on the abdominal muscles can weaken them and create conditions conducive to hernia formation.
Types of Hernias:
Inguinal Hernia:
The most common type of hernia, an inguinal hernia, occurs when a portion of the intestine protrudes through a weak spot or tear in the abdominal wall. This type is more prevalent in men.
Femoral Hernia:
Similar to an inguinal hernia, a femoral hernia occurs when tissue protrudes into the canal that carries the femoral artery and vein from the abdomen to the thigh. This type is more common in women.
Hiatal Hernia:
Hiatal hernias involve the stomach protruding through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. They can contribute to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) symptoms.
Umbilical Hernia:
Occurring near the navel, an umbilical hernia involves tissue or part of the intestine pushing through a weakened abdominal wall. This type is more common in infants.
Incisional Hernia:
Developing at the site of a previous abdominal surgery, an incisional hernia involves tissue pushing through a weakened scar or incision in the abdominal wall.
Common Symptoms of Hernias:
Visible Bulge:
The most recognizable symptom of a hernia is a visible bulge or lump at the site of the protrusion, especially when standing, coughing, or straining.
Discomfort or Pain:
Individuals with hernias may experience discomfort or pain at the site of the bulge, which can range from mild to severe.
Pressure or Heaviness:
Some people describe a sensation of pressure or heaviness in the affected area, particularly after prolonged standing or physical exertion.
Changes in Bowel Habits:
In certain cases, hernias can cause changes in bowel habits, including constipation or difficulty with bowel movements.
Nausea and Vomiting:
Hiatal hernias, in particular, can lead to symptoms such as nausea and vomiting due to the involvement of the stomach in the chest cavity.
Diagnosis of Hernias:
Physical Examination:
A healthcare provider can often diagnose a hernia through a physical examination, where they may palpate the affected area and observe any visible bulges or lumps.
Medical History:
A detailed medical history helps healthcare providers understand the nature and duration of symptoms, contributing factors, and potential risk factors for hernia development.
Imaging Studies:
Various imaging studies may be employed to visualize the hernia more clearly and assess its size and location. Ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI scans are common diagnostic tools.
Endoscopy:
In cases of hiatal hernias or suspected internal hernias, endoscopy may be used to directly visualize the affected area using a flexible tube with a camera.
Treatment Options for Hernias:
Watchful Waiting:
In some cases, especially if the hernia is small and not causing significant symptoms, a healthcare provider may recommend a watchful waiting approach. Regular monitoring and lifestyle modifications may be advised.
Hernia Belts or Trusses:
For individuals with reducible hernias, where the protruding tissue can be pushed back into place, hernia belts or trusses may provide support and help alleviate symptoms. However, these are usually considered temporary solutions.
Lifestyle Changes:
Adopting lifestyle changes can be beneficial in managing hernia symptoms. This may include maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding heavy lifting, practicing good posture, and addressing conditions like constipation.
Medications:
Over-the-counter or prescription medications may be recommended to manage symptoms associated with hernias, such as pain or discomfort. However, medications do not address the hernia itself.
Surgery:
Surgical intervention is often considered the most effective treatment for hernias, especially if they are causing significant symptoms or complications. There are different surgical approaches, including traditional open surgery and minimally invasive procedures like laparoscopic surgery.
Open Surgery:
In open surgery, a larger incision is made to repair the hernia by returning the protruding tissue to its original position and reinforcing the weakened muscles or tissues.
Laparoscopic Surgery:
This minimally invasive approach involves smaller incisions and the use of a camera and specialized instruments to repair the hernia. Laparoscopic surgery often results in shorter recovery times and reduced postoperative pain.
Prevention and Outlook:
While not all hernias can be prevented, adopting a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of developing certain types of hernias. Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding heavy lifting, practicing proper lifting techniques, and addressing conditions that contribute to muscle weakness can contribute to hernia prevention.
In conclusion, hernias are a common medical condition with various types and causes. Recognizing the symptoms, obtaining a timely diagnosis, and exploring appropriate treatment options are crucial steps in managing hernias effectively. If you suspect you have a hernia or are experiencing symptoms associated with hernias, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan. With advancements in medical techniques and a range of treatment options available, individuals diagnosed with hernias can explore tailored approaches to alleviate symptoms and promote long-term well-being.
About the Author:
Meet Dr. Rahul Raghavapuram, a leading Surgical Gastroenterologist in Hyderabad. With an MBBS, DNB in General Surgery, and DNB in Surgical Gastroenterology, he excels in providing top-notch healthcare. Dr. Raghavapuram, affiliated with IRA Gastro and Surgery Clinic, Meerpet, Hyderabad, holds prestigious fellowships in FACRSI, FMAS, and FIAGES, showcasing his commitment to excellence. Renowned for his proficiency in general and surgical gastroenterology, Dr. Raghavapuram combines extensive medical knowledge with a patient-centered approach. His dedication to staying abreast of medical advancements ensures patients receive cutting-edge care. As the go-to Surgical Gastroenterologist, he continues to positively impact lives at IRA Gastro and Surgery Clinic.